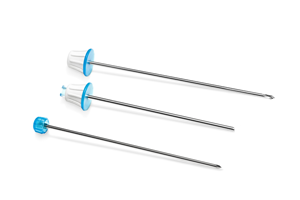
Coaxial bone biopsy system
In 2012, the popular, worldwide used Bonopty® family got a new member – Bonopty® 12G. Incorporating all the benefits of Bonopty® 14G, and adding some all new features.
- New, larger gauge gains access into the bone, even through thick cortical bone
- Coaxial system facilitates multiple sampling, or treatment of lesions
- Achieve excellent core samples with few crush artifacts
- Successfully sample somewhat sclerotic lesions
- Secure sample in biopsy cannula during retrieval using Core Lock